# Custom Alerts
The key performance metrics of data is monitored and messages are pushed in case of exceptions, helping you identify problems in a timely manner and reducing unnecessary losses. With Metric Alert, you may pay attention to:
- Whether core features of the product operate properly
- Whether business performance lives up to expectation
- Whether the product ecosystem is healthy enough.
# Create alerts
You may directly add analytical metrics to create alerts at 「 Applications → Custom Alerts」 on the upper part of the navigation bar or at Event Analysis.
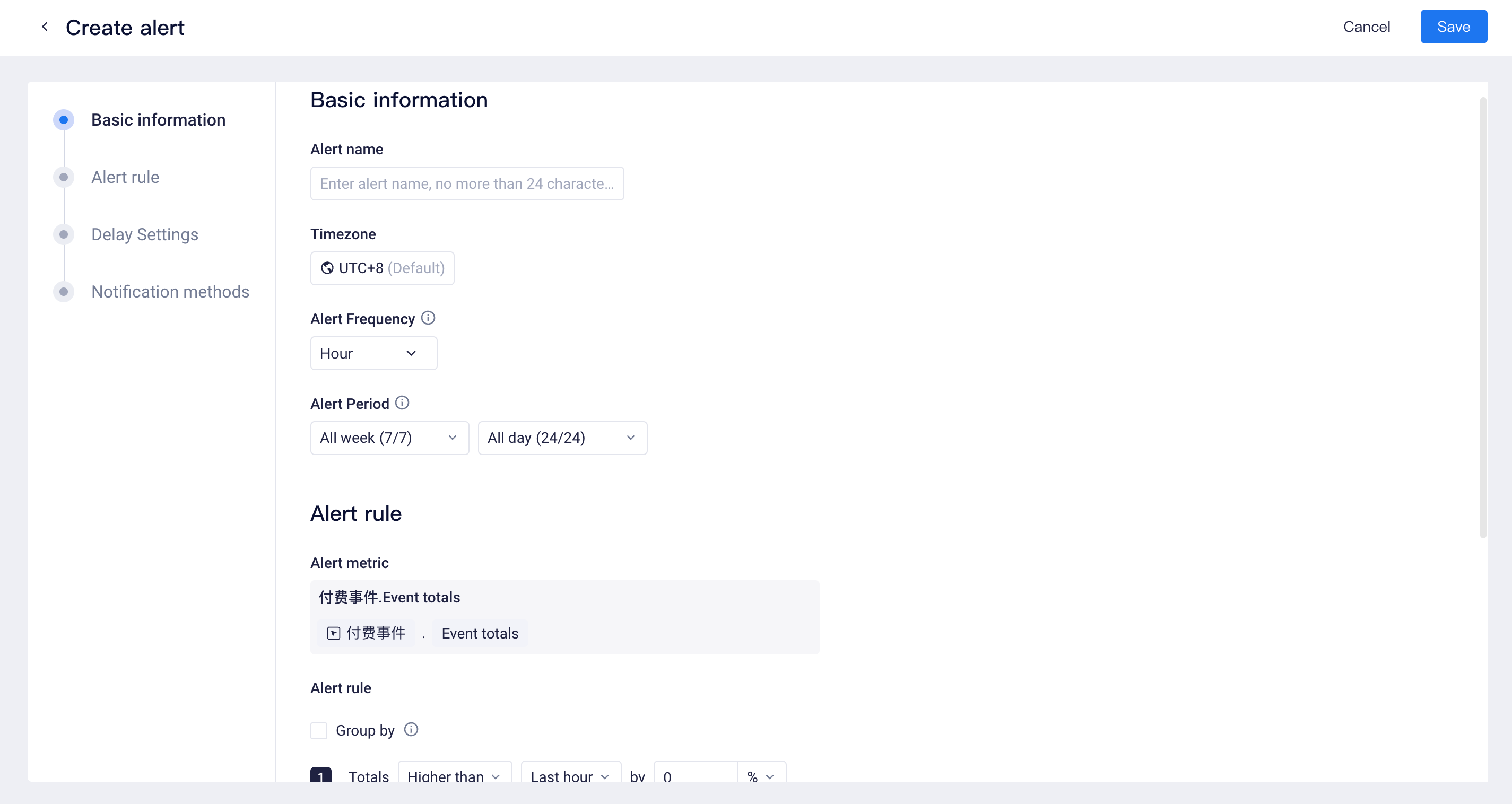
# Basic information
Alert Name: Up to 24 characters.
Timezone: Select the settlement time zone for the alert metrics. This option is available when
Project Timezone is enabled.
Alert Frequency: choose to execute the alert task "by hour" or "by day".
Alert Period: The monitoring metric values generally fluctuate over time. For example, most products have fewer active users in the early morning, which means that alert rules targeting regular periods of time may not work. In this scenario, alert time frames can be configured not to send alert notifications during early morning.
# Alert rule
# Alert metrics
You can add simple metrics or edit equation-based metrics.
You can add the "group-by" term to specify metric values of different groups in monitoring.
# Trigger rules
You may judge whether there are exceptional movements in metrics by the following rules:
- Compare with fixed values: Compare data with fixed values, anything higher or lower than fixed values can be determined as exceptions.
- For example, alert can be initiated when the number of active users is lower than a fixed value.
- This is suitable for periods when business is stable.
- Compare with relative values: Compare data with those of the previous period.
- For example, alert can be initiated when the number of active users is lower than the same period of the previous day.
- This is suitable for steadily growing business.
- Compare with statistic distributions: Compare data with mean metric values of the past period.
- For example, alert can be initiated when the number of active users is lower than the mean value during the past 24 hours.
- In comparison with "compare with relative values", this approach is advantageous as it can eliminate the effect of single anomalies on alert judgment.
- Based on prediction value: Alert is initiated when data is higher than the upper limit or lower than the lower limit of the prediction value.
- If there are no definitive monitoring rules, you may select alert by predication values.
- The prediction model adopts the Hannan-Rissanen algorithm, the academic paper of which is shown in this Document (opens new window).
# Delay Setting
There is a transmission process between data generation and storage. To ensure the integrity of statistical data of alert tasks, you may incorporate an appropriate delay in alert task computation based on actual delay of project data.
- For example, if the monitoring is implemented by hour and the delay time is set as 15 minutes, then the 6:00 alert task will be executed at 6:15.
- If the monitoring is implemented by day and the delay time is set as 30 minutes, then the daily alert task will be executed at 0:30 of the following day.
# Notification mode
Multiple notification channels are supported.
# Manage alerts
# Number of alert tasks
A maximum of 50 metric alert tasks can be running simultaneously within a project and new tasks exceeding this limit will not be saved.
# Use permissions
| Permission details | Root | Project Owner | Analysis Admin | Analys | Regular Members |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View the alert management list | ● | ● | ● | △ | ○ |
| Add, edit or delete self-created alert tasks | ● | ● | ● | △ | ○ |
| Add, edit or delete alert tasks created by others | ● | ● | ● | △ | ○ |
Notes on permissions:
● Compulsory availability to roles
▲ Availability by default for roles, but unavailability is allowed
△ Unavailability for roles by default, but availability is allowed
○ Compulsory unavailability for roles
